简介
在计算机处理计算时,由于计算机的确定性,随机性是一个重要但难以处理的问题。说到区块链,情况更是如此,因为计算机不仅是确定性的,而且是透明的。因此,由于随机性将在链上计算,而链是所有矿工和用户的公共信息,因此无法生成可靠的本机随机数。
所以我们可以使用一些web2技术来生成随机性,然后在链上使用它们。
什么是oracle(预言机)?
-
预言机是将数据从外部世界发送到区块链的智能合约,反之亦然。
-
然后,智能合约可以使用这些数据做出决定并改变其状态。
-
它们作为区块链和外部世界之间的桥梁。
-
然而,需要注意的是,区块链预言机本身不是数据源,它的工作是查询、验证和认证外部数据,然后再将其传递给智能合约。
今天我们将学习其中一个名为Chainlink VRF的预言机。
开始吧🚀
介绍
-
Chainlink VRF 用来产生随机值的预言机。
-
这些数值是用加密证明来验证的。
-
这些证明验证了结果没有被预言机操作员、用户、矿工等篡改或操纵。
-
证明是在链上公布的,因此可以被验证。
-
在验证成功后,它们会被要求随机性的智能合约所使用。
官方的Chainlink文档将VRF描述为。
Chainlink VRF(可验证的随机函数)是一个为智能合约设计的可证明的公平和可验证的随机性来源。智能合约开发者可以使用Chainlink VRF作为防篡改的随机数发生器(RNG),为任何依赖不可预测结果的应用构建可靠的智能合约。
它是如何工作的?
-
Chainlink有两个合约,我们主要关注的是VRFConsumerBase.sol和VRFCoordinator。
-
VRFConsumerBase是将调用VRF协调员的合同,它最终负责发布随机性。
-
我们将继承VRFConsumerBase,并将使用其中的两个函数。
- requestRandomness,它对随机性提出初始请求。
- fulfillRandomness,这是一个接收并对经过验证的随机性做一些事情的函数。
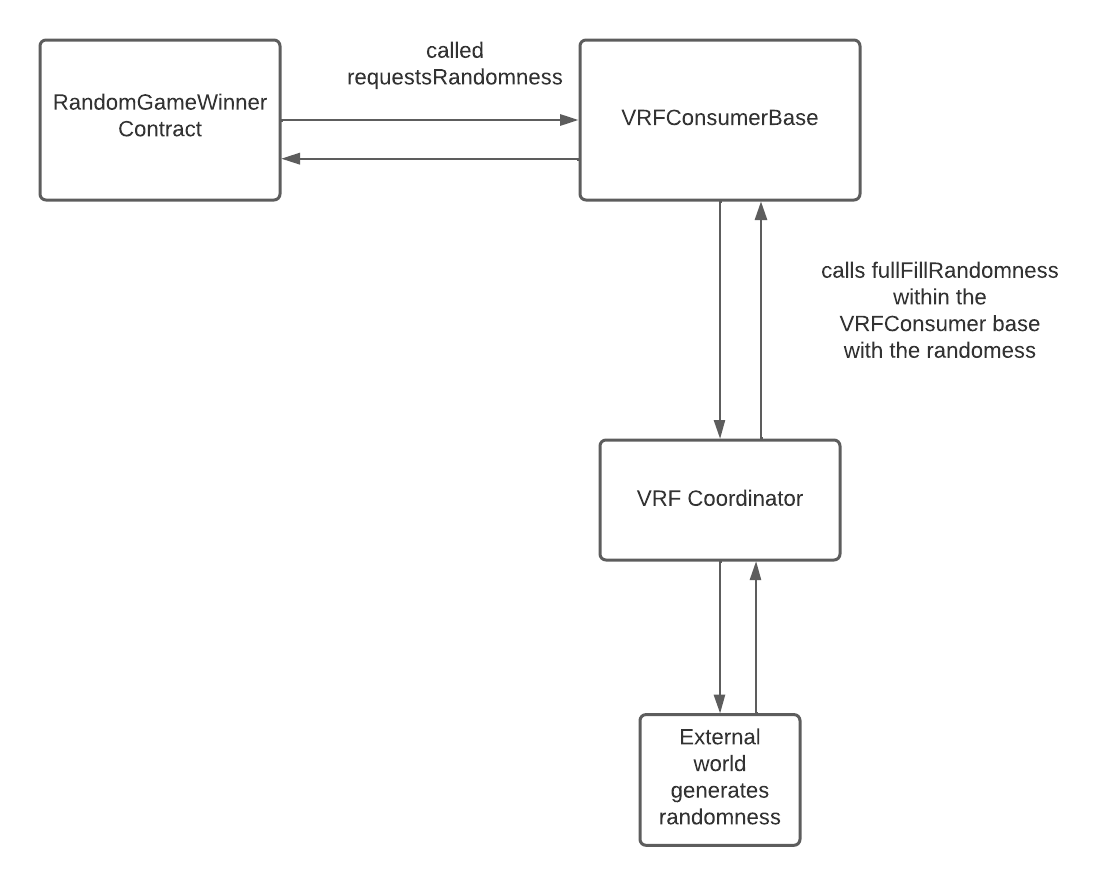
![https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/20220727220152.png https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/20220727220152.png]()
-
如果你看一下图,你就可以理解这个流程,RandomGameWinner合约将继承VRFConsumerBase合约,并将在VRFConsumerBase中调用requestRandomness函数。
-
在调用该函数时,对随机性的请求开始了,VRFConsumerBase进一步调用VRFCoordinator合约,该合约负责从外部世界获取随机性。
-
在VRFCoordinator获得随机性后,它调用VRFConsumerBase中的fullFillRandomness函数,然后进一步选择赢家。
-
注意重要的部分是,尽管你调用了 requestRandomness 函数,但你在 fullFillRandomness 函数中获得了随机性。
先决条件
要求
- 我们今天将开发一个彩 票游戏
- 每场比赛将有一个最大的玩家人数和参赛费
- 在最大数量的玩家进入游戏后,将随机选择一名获胜者。
- 赢家将获得
maxplayers*entryfee数额的ether ,以赢得游戏。
构建
-
最初开始时,在你的电脑中创建一个名为RandomWinnerGame的文件夹
-
为了构建智能合约,我们将使用Hardhat。Hardhat是一个Ethereum开发环境和框架,为Solidity的全栈开发而设计。简单地说,你可以编写你的智能合约,部署它们,运行测试,并调试你的代码。
-
要设置一个Hardhat项目,打开终端并在RandomWinnerGame文件夹内执行这些命令
1
2
3
4
|
mkdir hardhat-tutorial
cd hardhat-tutorial
npm init --yes
npm install --save-dev hardhat
|
- 选择
Create a Javascript project
- 在
Hardhat Project root下按下回车
- 如果你想添加一个
.gitignore,请按回车键询问。
Do you want to install this sample project's dependencies with npm (@nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox)?按下回车
现在你有一个准备好的hardhat项目了!
如果你不是在mac上,请做这个额外的步骤,也安装这些库 :)
1
|
npm install --save-dev @nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox
|
并对所有问题按回车键。
- 在同一个终端中,现在安装
@openzeppelin/contracts,因为我们要导入Openzeppelin的合同。
1
|
npm install @openzeppelin/contracts
|
- 我们还将验证我们的合同,所以让我们安装hardhat etherscan库
1
|
npm install --save-dev @nomiclabs/hardhat-etherscan
|
- 最后,我们将安装chainlink 合约,以使用chainlink VRF
1
|
npm install --save @chainlink/contracts
|
- 现在在
contracts目录内创建一个新文件,名为RandomWinnerGame.sol,并粘贴以下几行代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
|
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.4;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/access/Ownable.sol";
import "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/VRFConsumerBase.sol";
contract RandomWinnerGame is VRFConsumerBase, Ownable {
//Chainlink variables
// The amount of LINK to send with the request
uint256 public fee;
// ID of public key against which randomness is generated
bytes32 public keyHash;
// Address of the players
address[] public players;
//Max number of players in one game
uint8 maxPlayers;
// Variable to indicate if the game has started or not
bool public gameStarted;
// the fees for entering the game
uint256 entryFee;
// current game id
uint256 public gameId;
// emitted when the game starts
event GameStarted(uint256 gameId, uint8 maxPlayers, uint256 entryFee);
// emitted when someone joins a game
event PlayerJoined(uint256 gameId, address player);
// emitted when the game ends
event GameEnded(uint256 gameId, address winner,bytes32 requestId);
/**
* constructor inherits a VRFConsumerBase and initiates the values for keyHash, fee and gameStarted
* @param vrfCoordinator address of VRFCoordinator contract
* @param linkToken address of LINK token contract
* @param vrfFee the amount of LINK to send with the request
* @param vrfKeyHash ID of public key against which randomness is generated
*/
constructor(address vrfCoordinator, address linkToken,
bytes32 vrfKeyHash, uint256 vrfFee)
VRFConsumerBase(vrfCoordinator, linkToken) {
keyHash = vrfKeyHash;
fee = vrfFee;
gameStarted = false;
}
/**
* startGame starts the game by setting appropriate values for all the variables
*/
function startGame(uint8 _maxPlayers, uint256 _entryFee) public onlyOwner {
// Check if there is a game already running
require(!gameStarted, "Game is currently running");
// empty the players array
delete players;
// set the max players for this game
maxPlayers = _maxPlayers;
// set the game started to true
gameStarted = true;
// setup the entryFee for the game
entryFee = _entryFee;
gameId += 1;
emit GameStarted(gameId, maxPlayers, entryFee);
}
/**
joinGame is called when a player wants to enter the game
*/
function joinGame() public payable {
// Check if a game is already running
require(gameStarted, "Game has not been started yet");
// Check if the value sent by the user matches the entryFee
require(msg.value == entryFee, "Value sent is not equal to entryFee");
// Check if there is still some space left in the game to add another player
require(players.length < maxPlayers, "Game is full");
// add the sender to the players list
players.push(msg.sender);
emit PlayerJoined(gameId, msg.sender);
// If the list is full start the winner selection process
if(players.length == maxPlayers) {
getRandomWinner();
}
}
/**
* fulfillRandomness is called by VRFCoordinator when it receives a valid VRF proof.
* This function is overrided to act upon the random number generated by Chainlink VRF.
* @param requestId this ID is unique for the request we sent to the VRF Coordinator
* @param randomness this is a random unit256 generated and returned to us by the VRF Coordinator
*/
function fulfillRandomness(bytes32 requestId, uint256 randomness) internal virtual override {
// We want out winnerIndex to be in the length from 0 to players.length-1
// For this we mod it with the player.length value
uint256 winnerIndex = randomness % players.length;
// get the address of the winner from the players array
address winner = players[winnerIndex];
// send the ether in the contract to the winner
(bool sent,) = winner.call{value: address(this).balance}("");
require(sent, "Failed to send Ether");
// Emit that the game has ended
emit GameEnded(gameId, winner,requestId);
// set the gameStarted variable to false
gameStarted = false;
}
/**
* getRandomWinner is called to start the process of selecting a random winner
*/
function getRandomWinner() private returns (bytes32 requestId) {
// LINK is an internal interface for Link token found within the VRFConsumerBase
// Here we use the balanceOF method from that interface to make sure that our
// contract has enough link so that we can request the VRFCoordinator for randomness
require(LINK.balanceOf(address(this)) >= fee, "Not enough LINK");
// Make a request to the VRF coordinator.
// requestRandomness is a function within the VRFConsumerBase
// it starts the process of randomness generation
return requestRandomness(keyHash, fee);
}
// Function to receive Ether. msg.data must be empty
receive() external payable {}
// Fallback function is called when msg.data is not empty
fallback() external payable {}
}
|
- 构造函数接收以下参数。
vrfCoordinator,是VRFCoordinator合同的地址。linkToken是链接令牌的地址,它是chainlink 获取其付款的令牌。vrfFee是发送随机性请求所需的链接令牌的数量vrfKeyHash,这是生成随机性的公钥的ID。这个值负责为我们的随机性请求生成一个唯一的ID,称为requestId。
(所有这些数值都是由Chainlink提供给我们的)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
/**
* startGame starts the game by setting appropriate values for all the variables
*/
function startGame(uint8 _maxPlayers, uint256 _entryFee) public onlyOwner {
// Check if there is a game already running
require(!gameStarted, "Game is currently running");
// empty the players array
delete players;
// set the max players for this game
maxPlayers = _maxPlayers;
// set the game started to true
gameStarted = true;
// setup the entryFee for the game
entryFee = _entryFee;
gameId += 1;
emit GameStarted(gameId, maxPlayers, entryFee);
}
|
onlyOwner函数意味着它只能由所有者调用。- 这个函数用于开始游戏,在这个函数被调用后,玩家可以进入游戏,直到达到极限。
- 它还会触发
GameStarted事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
/**
joinGame is called when a player wants to enter the game
*/
function joinGame() public payable {
// Check if a game is already running
require(gameStarted, "Game has not been started yet");
// Check if the value sent by the user matches the entryFee
require(msg.value == entryFee, "Value sent is not equal to entryFee");
// Check if there is still some space left in the game to add another player
require(players.length < maxPlayers, "Game is full");
// add the sender to the players list
players.push(msg.sender);
emit PlayerJoined(gameId, msg.sender);
// If the list is full start the winner selection process
if(players.length == maxPlayers) {
getRandomWinner();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
/**
* getRandomWinner is called to start the process of selecting a random winner
*/
function getRandomWinner() private returns (bytes32 requestId) {
// LINK is an internal interface for Link token found within the VRFConsumerBase
// Here we use the balanceOF method from that interface to make sure that our
// contract has enough link so that we can request the VRFCoordinator for randomness
require(LINK.balanceOf(address(this)) >= fee, "Not enough LINK");
// Make a request to the VRF coordinator.
// requestRandomness is a function within the VRFConsumerBase
// it starts the process of randomness generation
return requestRandomness(keyHash, fee);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
/**
* fulfillRandomness is called by VRFCoordinator when it receives a valid VRF proof.
* This function is overrided to act upon the random number generated by Chainlink VRF.
* @param requestId this ID is unique for the request we sent to the VRF Coordinator
* @param randomness this is a random unit256 generated and returned to us by the VRF Coordinator
*/
function fulfillRandomness(bytes32 requestId, uint256 randomness) internal virtual override {
// We want out winnerIndex to be in the length from 0 to players.length-1
// For this we mod it with the player.length value
uint256 winnerIndex = randomness % players.length;
// get the address of the winner from the players array
address winner = players[winnerIndex];
// send the ether in the contract to the winner
(bool sent,) = winner.call{value: address(this).balance}("");
require(sent, "Failed to send Ether");
// Emit that the game has ended
emit GameEnded(gameId, winner,requestId);
// set the gameStarted variable to false
gameStarted = false;
}
|
-
这个函数从VRFConsumerBase继承而来。它由VRFCoordinator合约在接收到外部世界的随机性后调用。
-
在接收到随机性(可以是uint256范围内的任何数字)后,我们使用mod 操作符从范围从0 to players.length-1取值
-
这就为我们选择了一个索引,我们用这个索引从玩家数组中检索出赢家。
-
它将合约中所有的ether 发送给赢家,并发出一个GameEnded事件。
-
现在我们要安装dotenv包,以便能够导入env文件并在我们的配置中使用它。打开一个终端,指向hardhat-tutorial目录,执行以下命令
- 现在在
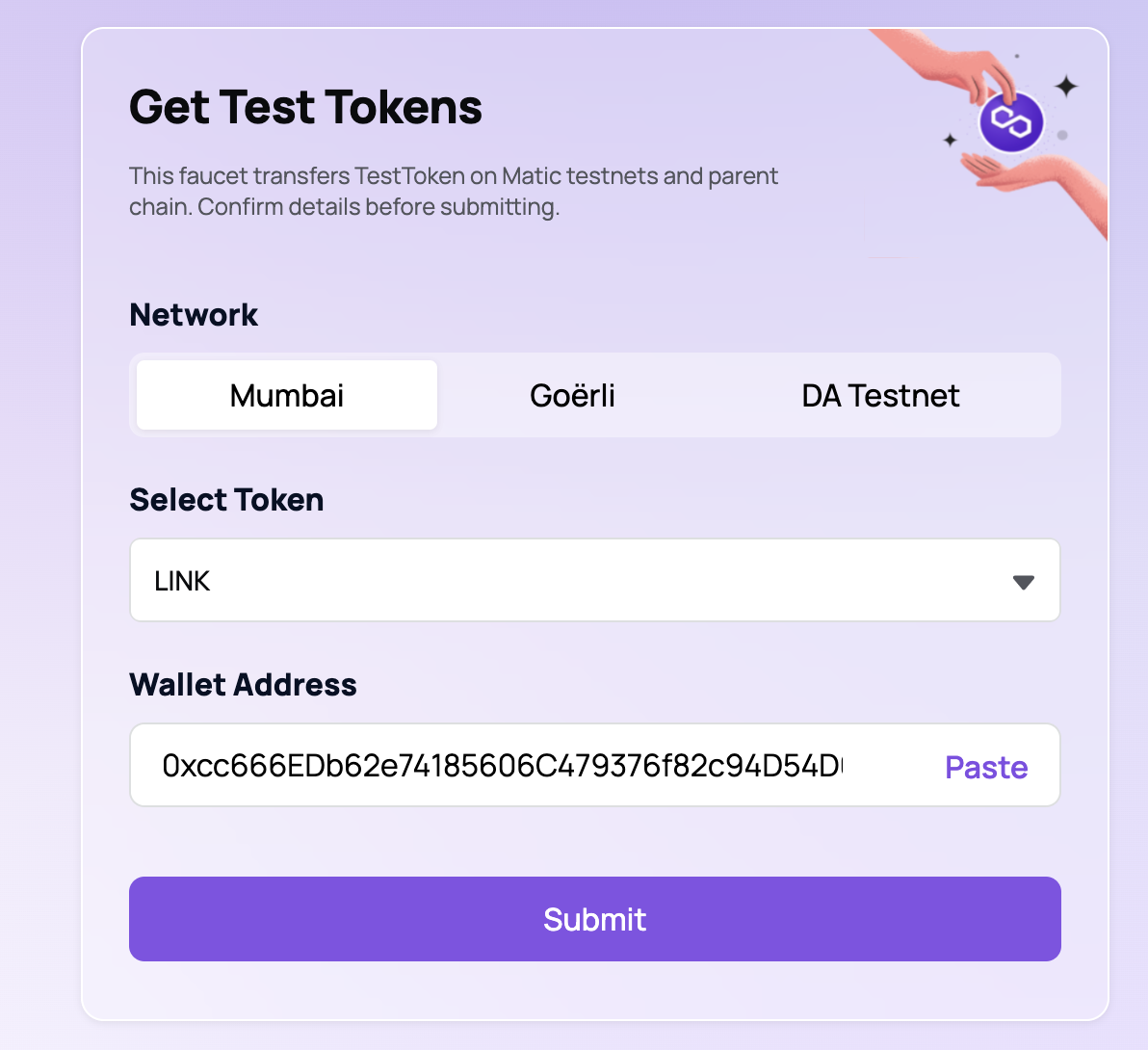
hardhat-tutorial文件夹下创建一个.env文件,并添加以下几行,使用注释中的说明来获得你的ALCHEMY_API_KEY_URL、MUMBAI_PRIVATE_KEY和POLYGONSCAN_KEY.如果你的MetaMask上没有mumbai ,你可以按照这个来把它添加到你的MetaMask上,确保你获得mumbai 私钥的账户有mumbai Matic资金,你可以从这里得到一些。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
// Go to https://www.alchemyapi.io, sign up, create
// a new App in its dashboard and select the network as Mumbai, and replace "add-the-alchemy-key-url-here" with its key url
ALCHEMY_API_KEY_URL="add-the-alchemy-key-url-here"
// Replace this private key with your Mumbai account private key
// To export your private key from Metamask, open Metamask and
// go to Account Details > Export Private Key
// Be aware of NEVER putting real Ether into testing accounts
MUMBAI_PRIVATE_KEY="add-the-mumbai-private-key-here"
// Go to https://polygonscan.com/, sign up, on your account overview page,
// click on `API Keys`, add a new API key and copy the
// `API Key Token`
POLYGONSCAN_KEY="add-the-polygonscan-api-token-here"
|
- 现在打开
hardhat.config.js文件,我们将在这里添加mumbai网络,这样我们就可以把我们的合同部署到mumbai,还有一个etherscan对象,这样我们就可以在polygonscan上验证我们的合同。将hardhat.config.js文件中的所有行替换为下面给出的行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
require("@nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox");
require("dotenv").config({ path: ".env" });
require("@nomiclabs/hardhat-etherscan");
const ALCHEMY_API_KEY_URL = process.env.ALCHEMY_API_KEY_URL;
const MUMBAI_PRIVATE_KEY = process.env.MUMBAI_PRIVATE_KEY;
const POLYGONSCAN_KEY = process.env.POLYGONSCAN_KEY;
module.exports = {
solidity: "0.8.9",
networks: {
mumbai: {
url: ALCHEMY_API_KEY_URL,
accounts: [MUMBAI_PRIVATE_KEY],
},
},
etherscan: {
apiKey: {
polygonMumbai: POLYGONSCAN_KEY,
},
},
};
|
- 创建一个名为
constants的新文件夹,并在其中添加一个名为index.js的新文件。在index.js文件中添加这些行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
const { ethers, BigNumber } = require("hardhat");
const LINK_TOKEN = "0x326C977E6efc84E512bB9C30f76E30c160eD06FB";
const VRF_COORDINATOR = "0x8C7382F9D8f56b33781fE506E897a4F1e2d17255";
const KEY_HASH =
"0x6e75b569a01ef56d18cab6a8e71e6600d6ce853834d4a5748b720d06f878b3a4";
const FEE = ethers.utils.parseEther("0.0001");
module.exports = { LINK_TOKEN, VRF_COORDINATOR, KEY_HASH, FEE };
|
我们从这里得到的数值,已经由Chainlink提供给我们。
- 让我们把合同部署到
mumbai网络。在scripts文件夹下创建一个新文件,或替换默认的现有文件,命名为deploy.js。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
const { ethers } = require("hardhat");
require("dotenv").config({ path: ".env" });
require("@nomiclabs/hardhat-etherscan");
const { FEE, VRF_COORDINATOR, LINK_TOKEN, KEY_HASH } = require("../constants");
async function main() {
/*
A ContractFactory in ethers.js is an abstraction used to deploy new smart contracts,
so randomWinnerGame here is a factory for instances of our RandomWinnerGame contract.
*/
const randomWinnerGame = await ethers.getContractFactory("RandomWinnerGame");
// deploy the contract
const deployedRandomWinnerGameContract = await randomWinnerGame.deploy(
VRF_COORDINATOR,
LINK_TOKEN,
KEY_HASH,
FEE
);
await deployedRandomWinnerGameContract.deployed();
// print the address of the deployed contract
console.log(
"Verify Contract Address:",
deployedRandomWinnerGameContract.address
);
console.log("Sleeping.....");
// Wait for etherscan to notice that the contract has been deployed
await sleep(30000);
// Verify the contract after deploying
await hre.run("verify:verify", {
address: deployedRandomWinnerGameContract.address,
constructorArguments: [VRF_COORDINATOR, LINK_TOKEN, KEY_HASH, FEE],
});
}
function sleep(ms) {
return new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
}
// Call the main function and catch if there is any error
main()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
|
- 编译合同,打开终端,指向
hardhat-tutorial目录,执行以下命令
- 要进行部署,请打开终端,指向hardhat-tutorial目录,并执行以下命令
1
|
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network mumbai
|
![https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/20220727223246.png https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/20220727223246.png]()
![https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/20220727223358.png https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/20220727223358.png]()
![https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/20220727223422.png https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/20220727223422.png]()
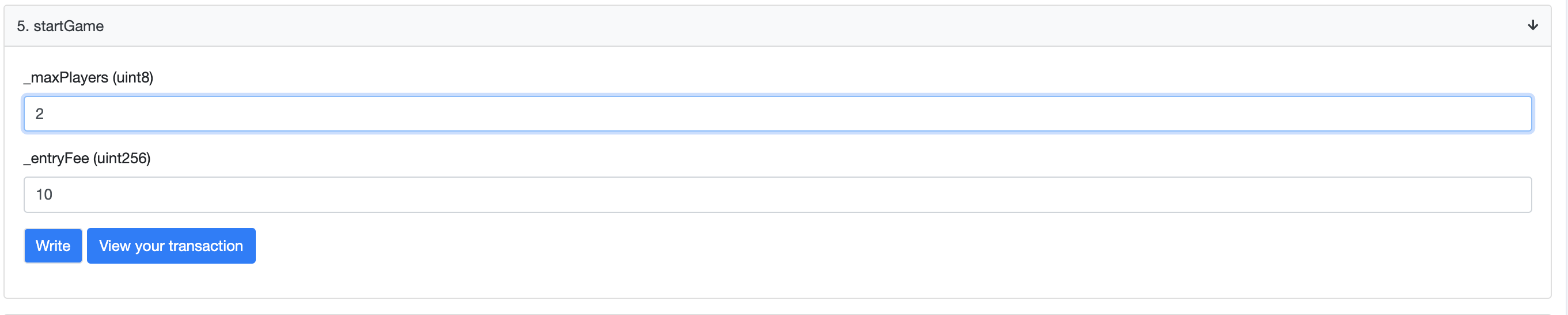
- 然后在startGame函数中输入一些数值,并点击Write按钮
![https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/20220727223446.png https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/20220727223446.png]()
![https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/20220727223459.png https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/20220727223459.png]()
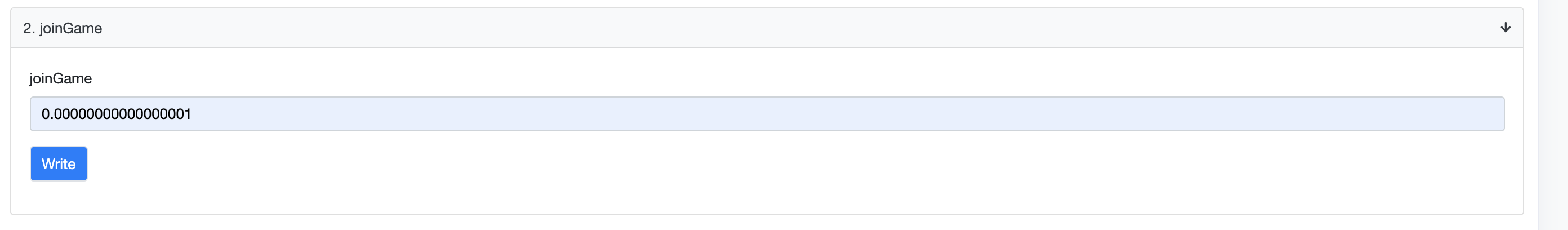
-
现在你可以用你的地址加入游戏了。注意:我在这里输入的数值是10WEI,因为这是我指定的报名费的数值,但是因为加入游戏接受ether 而不是WEI,我必须将10WEI转换成ether 。你也可以用eth转换器将你的参赛费转换成ether
-
现在刷新页面,并连接一个新的钱包,其中有一些matic,这样你就可以让另一个玩家加入。 注:我将最大玩家数设置为2,这样在我让另一个地址加入游戏后,它将选择赢家。
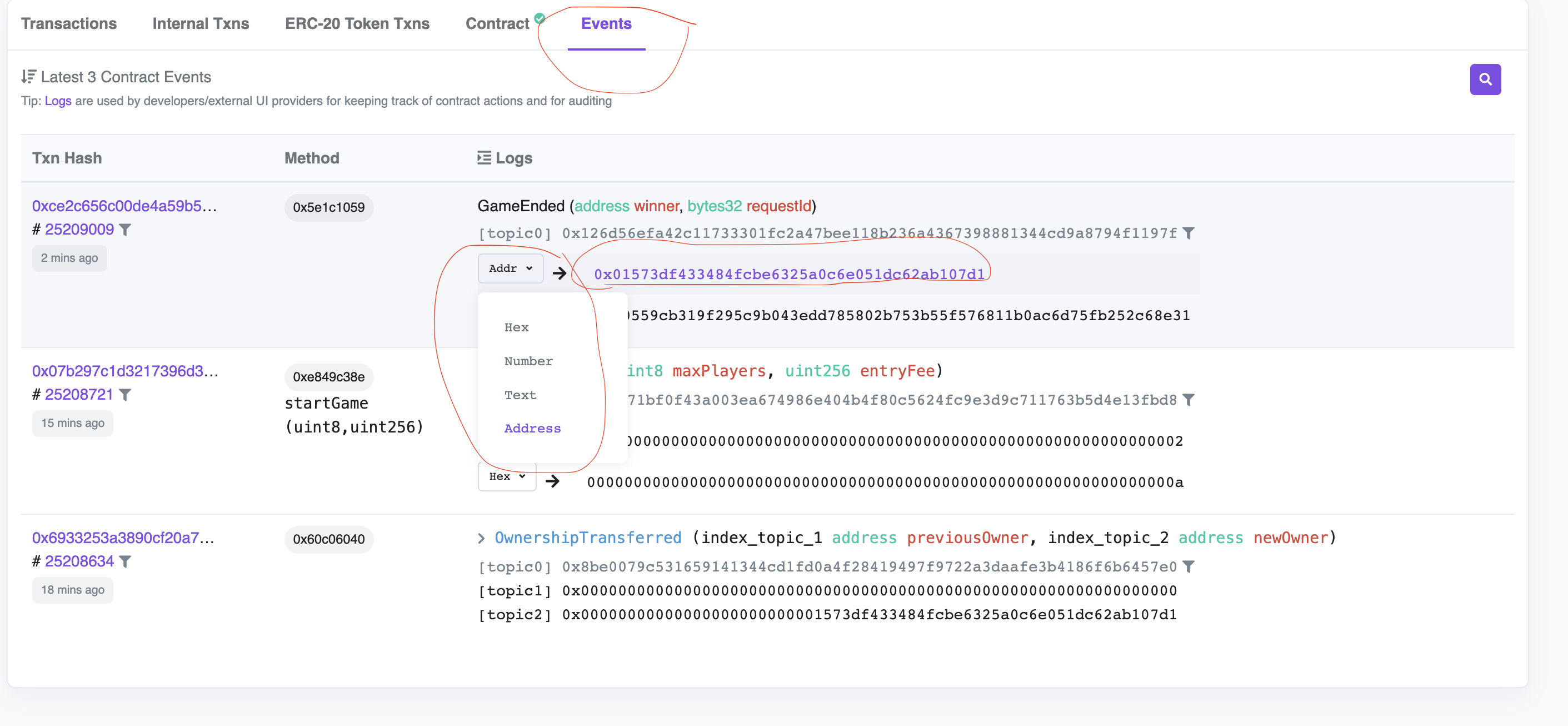
-
如果你现在进入你的事件选项卡并不断刷新(VRFCoordinator调用fullFillRandomness函数需要一些时间,因为它必须从外部世界获得数据),在某一时刻你将能够看到一个事件,上面写着GameEnded
-
从下拉菜单中为GameEnded事件中的第一个值转换Hex为地址,因为那是赢家的地址。
![https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/20220727223739.png https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/20220727223739.png]()
它完成了 🚀
你现在知道如何玩这个游戏了。在下一个教程中,我们将为此创建一个用户界面,并将学习如何使用代码本身来跟踪这些事件。
准备开始吧🚀🚀
原文: https://www.learnweb3.io/tracks/junior/chainlink-vrf
![https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/my.png https://hicoldcat.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/my.png]()